Hands-On Physio
Our physios are highly skilled in many different types of manual and hands-on therapies including dry needling, myofascial release, trigger point therapy, myofascial cupping, joint mobilisation and electrotherapies.
Our treatment goals are to help you feel better as quickly as possible by using various hands-on treatment techniques, which, once you're feeling a bit better, gives us the opportunity to address imbalances in strength & function to get you feeling great in the long term!
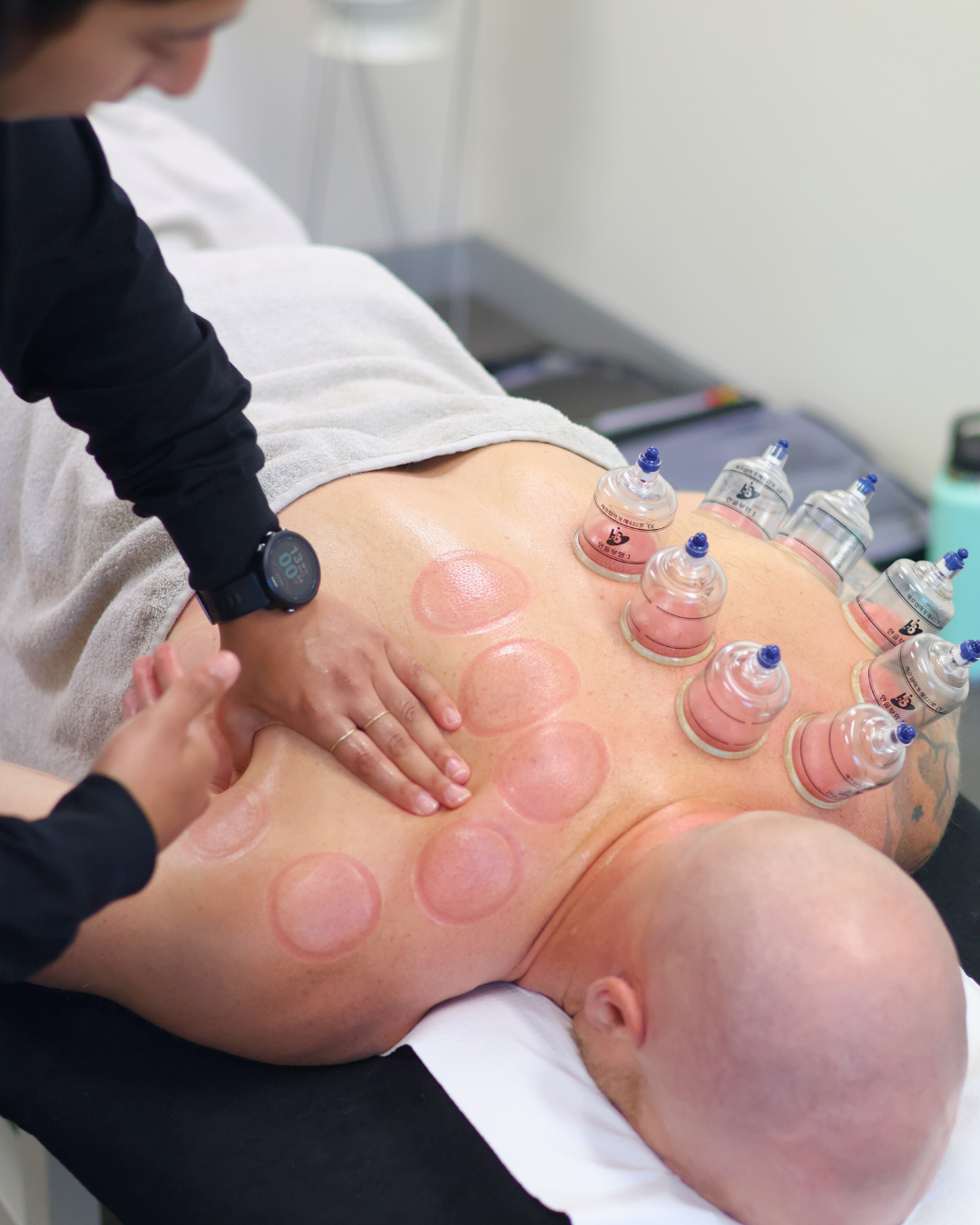
Myofascial Cupping
Myofascial cupping is a therapeutic technique that involves the use of suction cups on the skin to create a negative pressure or vacuum effect. This technique is often used to address issues related to the fascia, which is the connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, bones, and organs throughout the body.
Myofascial cupping is a therapeutic technique that involves the use of suction cups on the skin to create a negative pressure or vacuum effect. This technique is often used to address issues related to the fascia, which is the connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, bones, and organs throughout the body.
During myofascial cupping, the cups are typically made of silicone, plastic, or glass. The cups are placed on the skin and a vacuum is created by either suction or heat, drawing the skin and underlying tissue into the cup. This suction can help ease tension in the fascia, improve blood flow, and promote healing.
The negative pressure created by the cups is believed to lift and separate the layers of fascia, reducing adhesions and promoting the flow of fluids within the tissue. This may help alleviate muscle tension, improve range of motion, and reduce pain.
Myofascial cupping is sometimes combined with other techniques, such as massage or manual therapy, to enhance its effectiveness.
As with any therapeutic approach, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine whether myofascial cupping is appropriate for your specific needs and conditions.
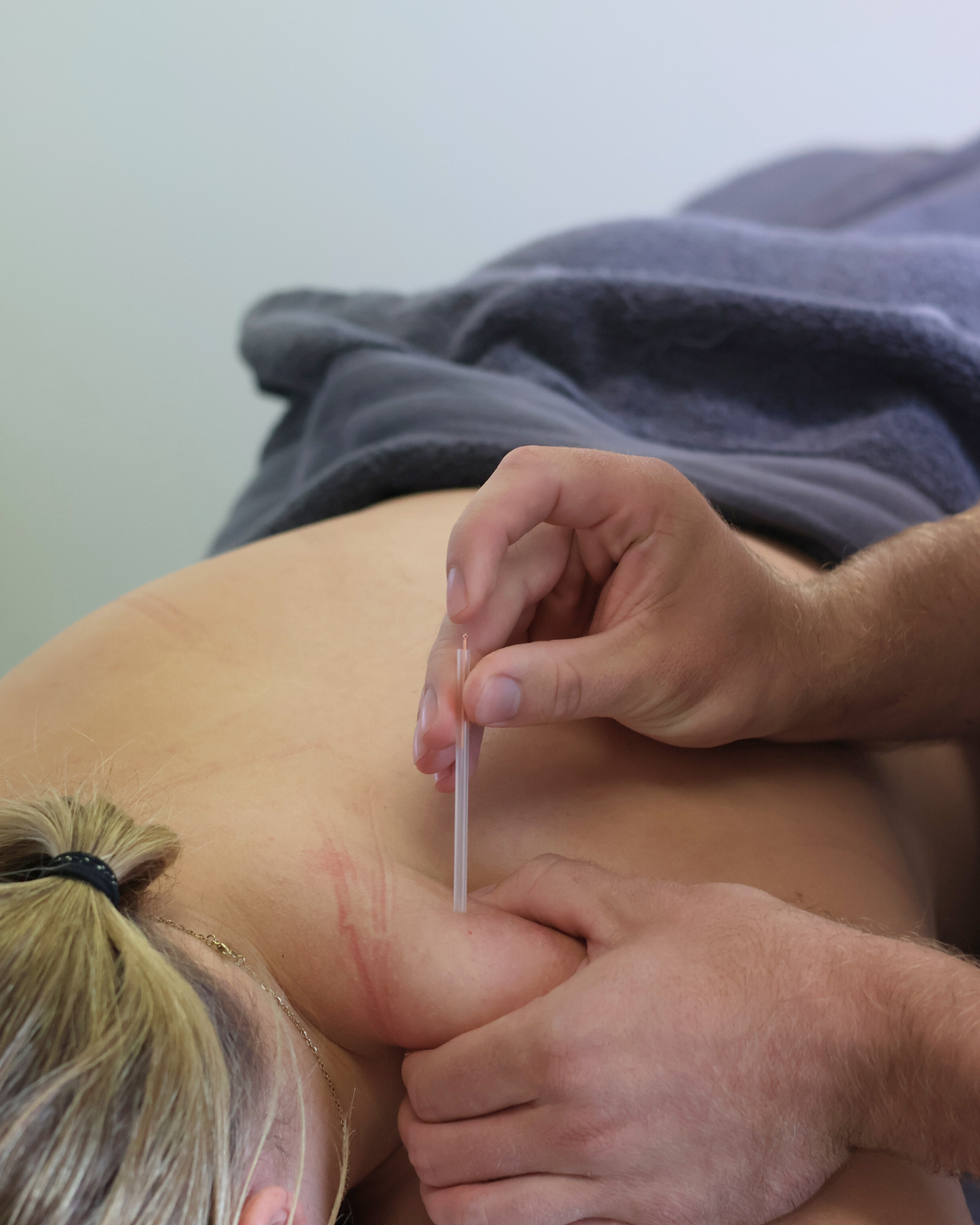
Electro-Muscular Dry Needling
Dry needling on its own is a great treatment tool for a range of conditions. It involves inserting fine acupuncture needles into trigger points in the muscles. Electro dry needling involves attaching electrode cables to end of these needles, which are attached to electrical stimulation machine. This sends an electric impulse through the needle, into the tissue, and can be excellent for reducing pain and sensitivity.
The addition of electrical stimulation (e-stim) helps to enhance the treatment pain relieving effect of dry needling. E-stim helps to stimulate blood flow and provide pain relief, often providing long-term relief of symptoms. The increased blood circulation also promotes the delivery of nutrients to tissues, accelerating the healing process.
What can it help with?
Electro dry needling can help treat a huge range of conditions including:
- Nerve: neuropathy, sciatica
- Soft tissue: spasm, strains, cramping, trigger points, tightness, plantar fasciitis
- Joint: sprains, arthritis, joint stiffness, disc pathologies, tendinitis
What Does it Feel Like?
This will depend on the frequency used and the desired results. It shouldn't be painful, but can be slightly uncomfortable, depending on the severity of the condition being treated.
The sensation will usually range somewhere between a slight buzzing feeling to an obvious rhythmic twitching sensation.

Joint Mobilisation
Joint mobilisation is a hands-on manual therapy technique aimed at improving joint movement, reducing pain, and restoring normal function. It involves gently moving a joint through its natural range of motion to address stiffness, restricted movement, or discomfort caused by injury, inflammation, or other musculoskeletal conditions.
How It Works:
Slow, controlled, and precise movements are used by our physios to target affected joints. This technique differs from joint manipulation, which involves a quick, high-velocity thrust. Joint mobilisation is gentler and focuses on gradually improving movement, making it suitable for those recovering from injury, experiencing pain, or needing a careful approach to joint function.
Benefits of Joint Mobilisation:
- Improved joint mobility in stiff or restricted joints.
- Reduced discomfort caused by joint dysfunction or abnormal movement patterns
- Helps restore normal movement patterns by encouraging smooth, coordinated movement of joints and surrounding tissues.
- Safe and gradual – mobilisation offers a controlled approach for sensitive joints or during early rehab stages.
When combined with strengthening & other manual therapies, joint mobilisation can be very helpful in relieving pain and restoring function.
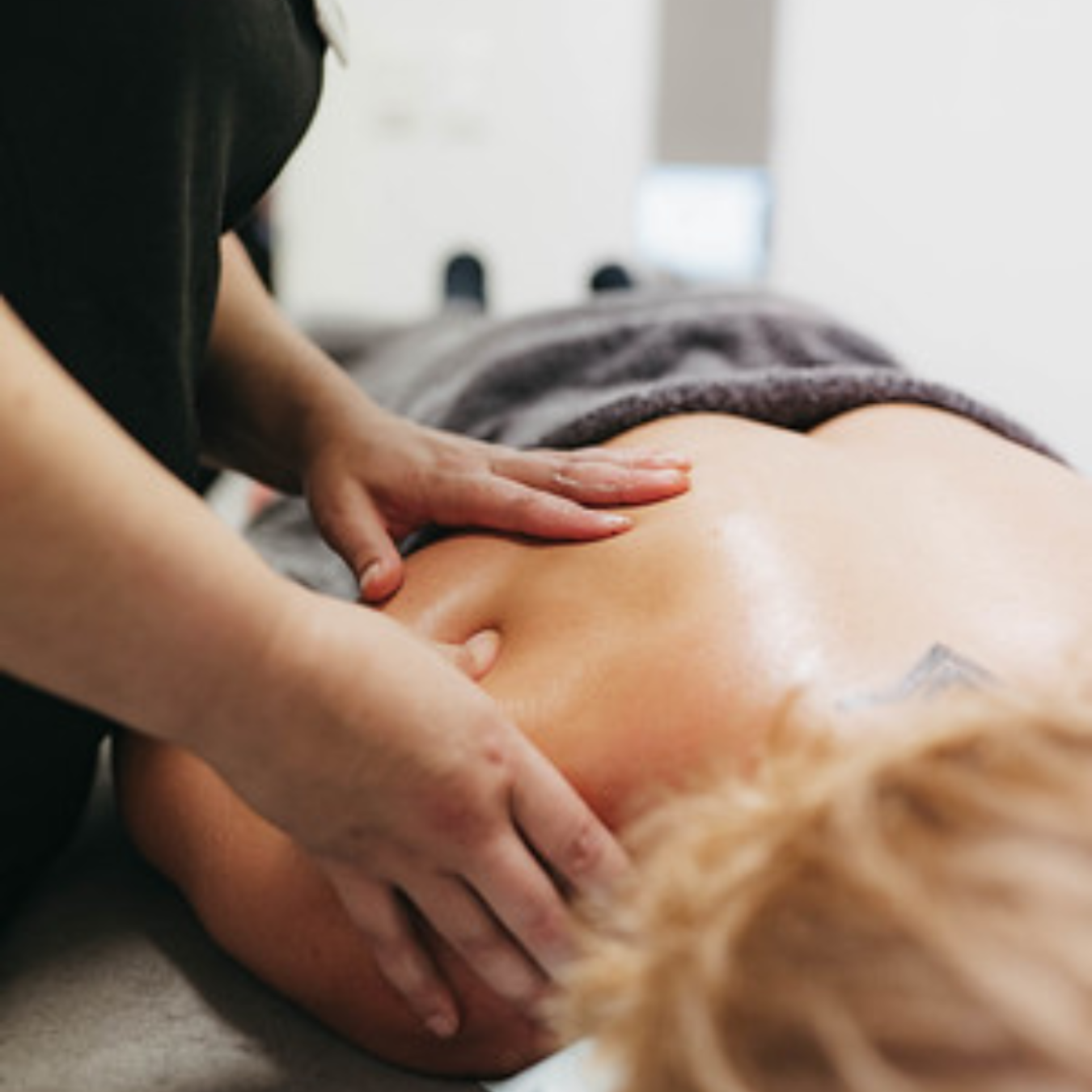
Trigger Point Therapy
Trigger point therapy, also known as myofascial trigger point therapy or trigger point massage, is a hands-on treatment that targets tight knots or “trigger points” within muscles. These areas of tension can be painful, sensitive, and sometimes refer discomfort to other parts of the body.
By applying sustained pressure to the affected points, this helps to ease the muscle tension, reduce pain, and restore normal movement. The therapist monitors the tissue closely, applying the pressure until the muscle softens and relaxes, promoting better overall muscle function.
Who Can Benefit?
- Anyone experiencing muscle stiffness or localized pain
- Those with referred pain caused by tight muscle knots
- People recovering from injury or managing chronic muscular tension
Benefits of Trigger Point Therapy:
- Helps ease acute or chronic pain caused by muscle tension.
- Encourages tight muscles to relax, improving flexibility and joint movement.
- Helps promote overall relaxation, easing stiffness and discomfort.
Myofascial Dry Needling
Dry needling is a hands-on therapeutic technique used to target myofascial trigger points and tight muscles, aiming to help to reduce pain, improve movement, and restore normal muscle function. It involves inserting thin needles into specific areas of muscle or connective tissue to release tension and improve mobility.
Unlike acupuncture, which is based on traditional Chinese medicine principles, dry needling is grounded in Western medicine and focuses on addressing specific and often localised musculoskeletal dysfunctions.
Benefits of Dry Needling:
- Pain Relief: Releases trigger points and eases muscular pain and tension.
- Improved Mobility: Enhances range of motion and functional movement.
- Supports Rehabilitation: Helps recovery from conditions such as myofascial pain syndrome, tension headaches, chronic pain, and musculoskeletal injuries.
- Safe and Targeted: Performed by trained physiotherapists with a focus on accuracy and client comfort.
- Complementary to Other Therapies: Works effectively alongside exercise therapy, manual techniques, and rehabilitation programs.
Dry needling can be a very effective tool for managing targeted muscular pain, improving movement quality, and supporting overall recovery in a safe and evidence-based manner.

Myofascial Release
Myofascial release is a hands-on manual therapy technique that focuses on releasing tension and restrictions within the fascia, the connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, bones, and organs. Tight or restricted fascia can result from trauma, inflammation, poor posture, or chronic muscular tension, potentially causing pain, reduced flexibility, and limited movement.
How It Works:
Our physiotherapists apply gentle, sustained pressure to specific areas of the fascia to release tightness and adhesions. This may involve direct manipulation of the fascia or indirect techniques using body positioning and movement. The therapist also relies on client feedback to monitor tissue response and ensure a safe, effective release.
Benefits of Myofascial Release:
- Relieves Pain: Reduces discomfort caused by tight fascia and muscle restrictions.
- Improves Flexibility and Range of Motion: Releases adhesions and tension to enhance movement.
- Promotes Relaxation: Eases stiffness and helps muscles function more effectively.
- Supports Recovery: Assists rehabilitation for conditions such as myofascial pain syndrome, chronic pain, and soft tissue restrictions.
- Safe and Adaptable: Gentle and controlled, suitable for sensitive areas or during early rehab stages.
When combined with strengthening, stretching, and other manual therapies, myofascial release can be highly effective in relieving pain, restoring movement, and improving overall musculoskeletal function.
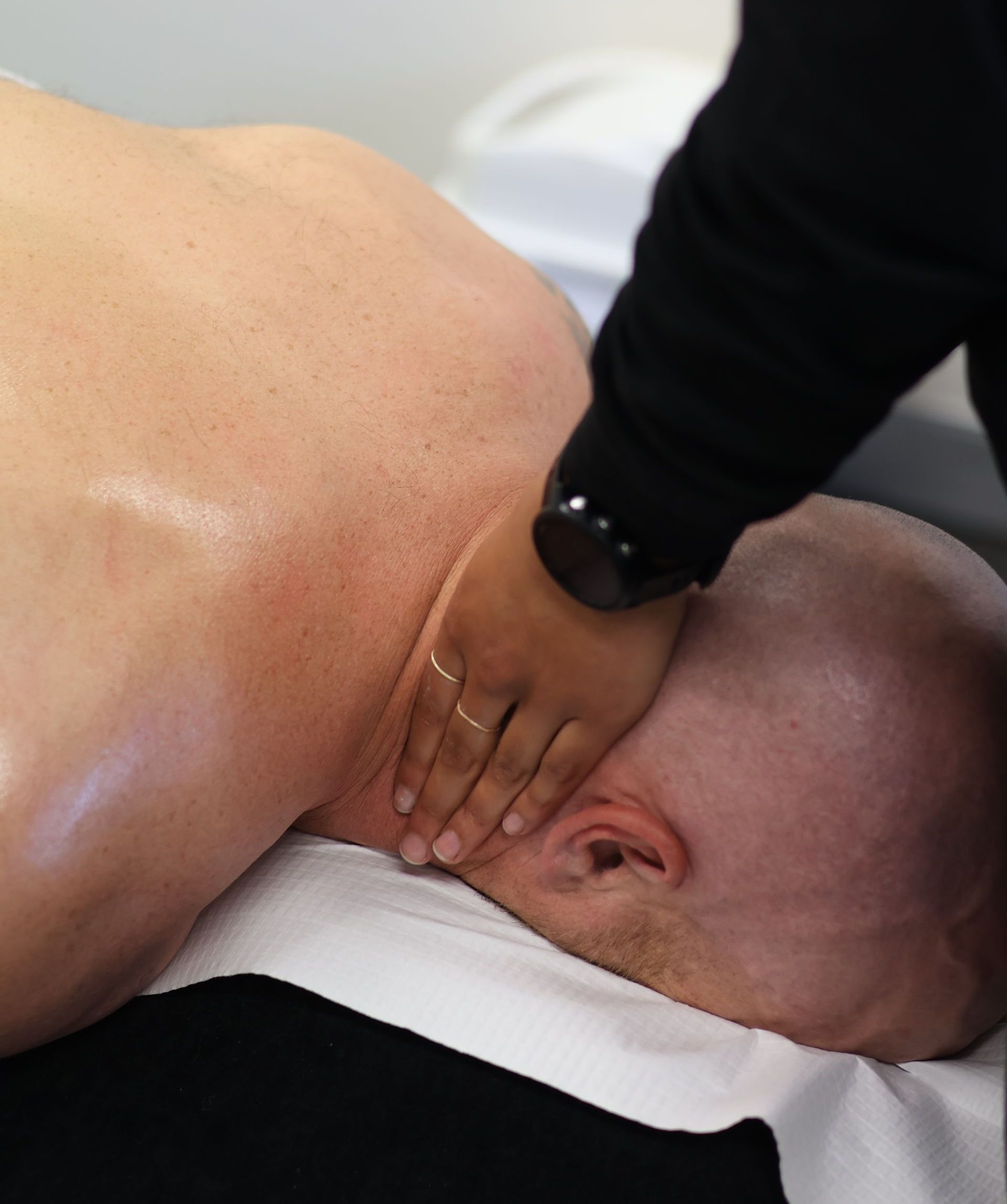
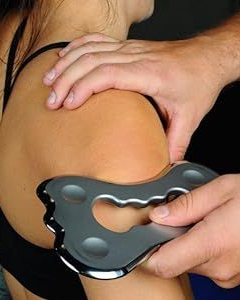
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilisation (IASTM)
IASTM is a hands-on manual therapy technique using specialised tools to target muscles, fascia, and connective tissue. It works by stimulating the nervous system to reduce tension, improve movement, and support functional recovery.
How It Works:
Our therapists use particular instruments to apply controlled pressure along affected areas. This stimulates neural pathways, helping muscles and fascia relax, improving proprioception, and enhancing mobility. While it may look intense, IASTM is generally not painful and is safe, gentle, and well-tolerated if done correctly.
Benefits of IASTM:
- Pain Relief: Reduces discomfort and tension in muscles and connective tissue.
- Improved Movement: Enhances range of motion and functional mobility.
- Supports Recovery: Assists rehabilitation from injuries or chronic muscular tightness.
- Restores Function: Promotes smooth, coordinated movement patterns.
- Safe and Reassuring: Though it may look intimidating, the treatment is gentle, controlled, and performed by trained physiotherapists.
When combined with strengthening, stretching, and other manual therapies, IASTM helps you move more freely, reduce pain, and support long-term recovery—without fear or discomfort.
